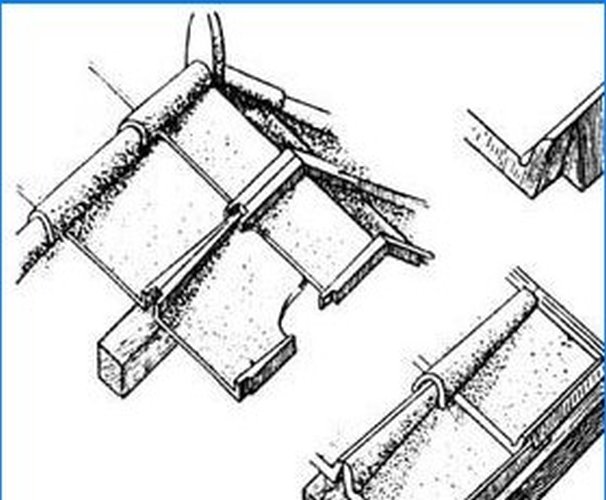
Fig. 1 Antique roof tiles.
Various forms of tiles and their corresponding methods of laying them have arisen in ancient times. The antique tile roof (Fig. 1) was laid in the same way as the modern one, along a wooden lathing, and consisted of two rows: the lower one, in the form of flat (trough-shaped) tiles, with ribs protruding on the sides, and the upper row. For the upper row, grooved tiles were used, which overlapped the joints of the underlying tiles. For the valleys, tiles of a special hexagonal shape were used, which correspond to the concave bend of the roof and ensure the correct flow of water (Fig. 2).
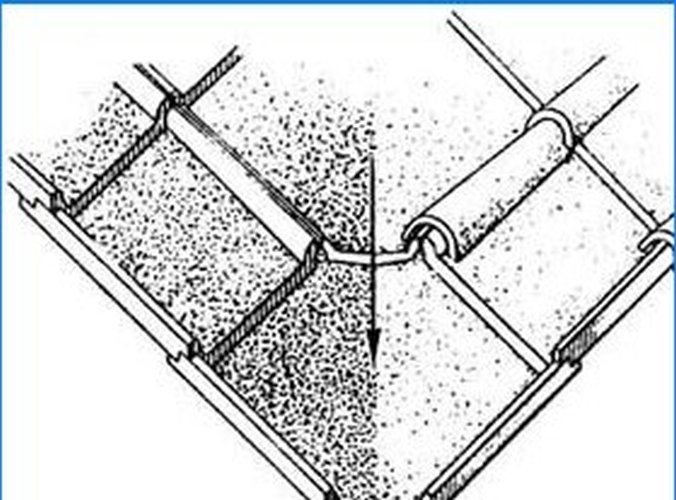
Fig. 2 Roof tiles for the valley (Pompeii).
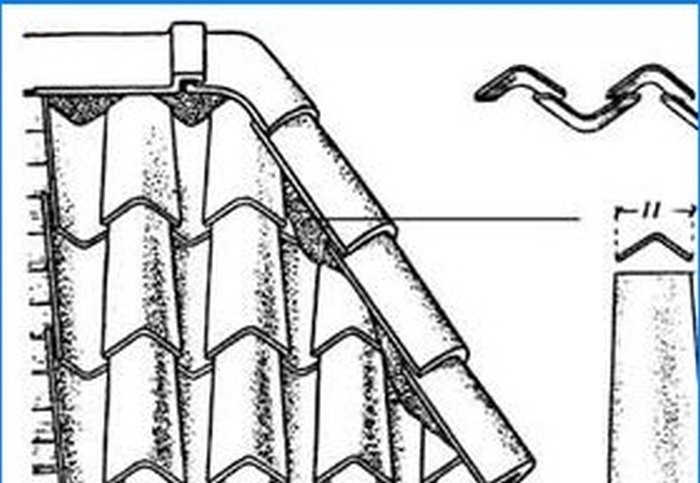
Fig. 3 Tatar tiles.
Varieties of flat (Fig. 4) and grooved tiles, similar to antique samples, have survived to this day. In the Crimea and the Caucasus, fluted shingles, known as Tatar shingles, were widespread (Fig. 3). And you can still find old houses covered with this material. It has the shape of halves of a truncated cone, and is laid along a solid plank formwork in two rows as follows: the tiles of the lower row are laid with the concave side up; upper – with the concave side downwards so that they overlap the joints of the tiles of the lower row. At the same time, the upper row of tiles rests on the lower row and is not attached to the crate, being held only by its own weight.
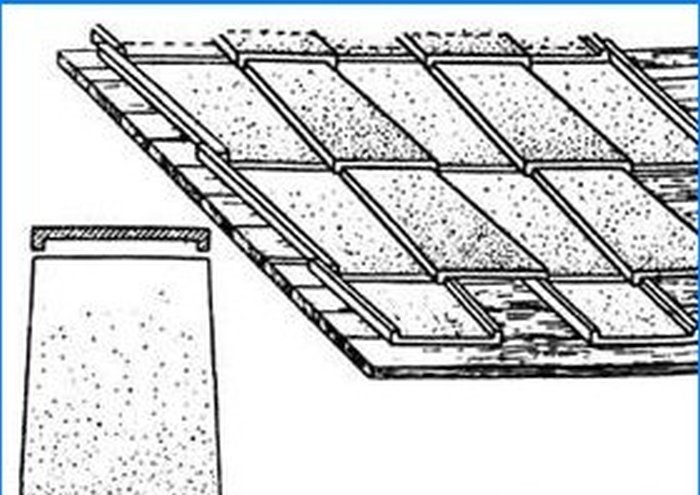
Fig. 4 Flat roof tiles.
S-shaped or as it is also called Dutch tiles are bent in the form of a wave (or the letter S), due to which each tile overlaps the adjacent adjacent one of the same row, and each of the rows overlaps the previous one (Fig. 5).
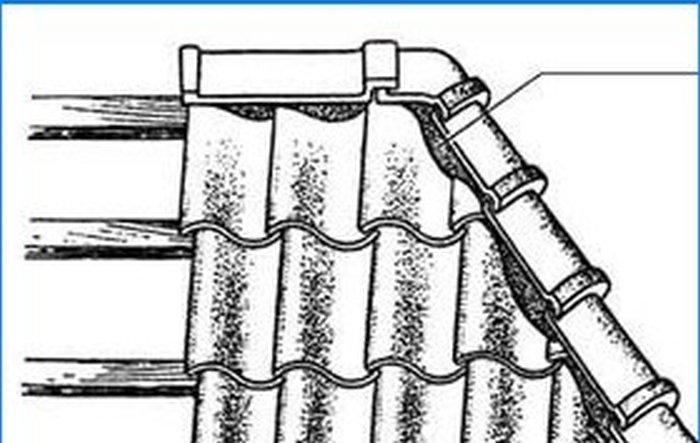
Fig. 5 Dutch roof tiles.
The disadvantage of grooved and Dutch tiles is too strong surface relief, which prevents snow from sliding, leading to its significant accumulation and subsequent descent in the form of an avalanche.

Fig. 6 Grooved undulating tiles (ORMAX).
Modern tiles are usually produced in three main types: flat, wavy (in the form of one or two waves) (Fig. 6) and grooved (also called a monk / nun) (Fig. 7). The shape of the tiles determines the way they are laid and the area of application..

Fig. 7 Roof tiles <monk / nun>: A – general view; B – installation.
Flat tiles are laid with a large overlap, moreover, there are several options for their installation: in two or even three layers. Flat and undulating shingles can be grooved, i.e. have special grooves along one or two edges. They provide a more secure fit as well as a waterproof roof. But their area of application is limited – only flat roofs. To create curved surfaces, grooved tiles are best suited, although smooth (no grooves) other shapes can be used..
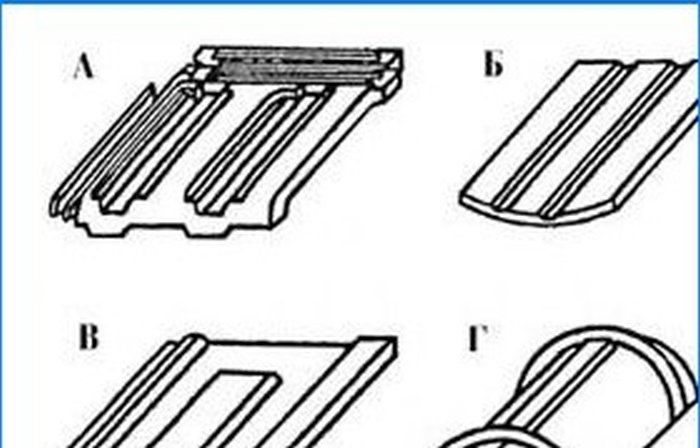
Fig. 8 Different types of tiles: A – groove stamped; B – flat; B – groove tape; G – ridge. 1 – longitudinal grooves; 2 – transverse grooves; 3 – groove rim.
There are two known technologies for the production of ceramic tiles: the strip method (Fig. 8B) and by stamping (Fig. 8A). Tape shingles are first formed into a tape which is then cut into individual shingles. Stamped tiles are immediately pressed into special metal molds. Tape slabs can have grooves only along the tiles, and stamped ones – both horizontally and vertically. Cement-sand tiles are produced only using tape technology.
The shape of the ceramic and cement-sand tiles are very similar, but differ in thickness. Ceramic tiles are thinner, more graceful, and cement-sand tiles are of greater thickness, their edge seems to be cut off. Leading manufacturers of cement-sand tiles are working to eliminate this shortcoming; the production of cement-sand tiles with a rounded edge has already been launched, which significantly increases its aesthetic appeal.

What are the different types of roof tiles available and how do they differ in terms of materials, durability, and aesthetics? Additionally, could you please explain the various methods of laying roof tiles and the advantages/disadvantages of each?
What are the different types of roof tiles available and how are they laid? I am curious to know more about the various materials and techniques used for installing roof tiles. Can you please provide some insights on this topic?
There are several types of roof tiles available, including clay tiles, concrete tiles, metal tiles, and slate tiles. Clay tiles are durable and have a traditional look, while concrete tiles are cheaper and come in various styles. Metal tiles are lightweight, long-lasting, and often used for modern designs. Slate tiles are expensive but offer a natural and elegant appearance. The installation techniques for roof tiles vary based on the material used. Generally, tiles are laid in rows starting from the bottom of the roof, overlapping each other to ensure water resistance. Rafters, battens, or a solid roof deck provide the base for the tiles. Flashings and ridge caps are used at the edges and peaks of the roof, respectively, to enhance waterproofing. It is important to follow manufacturer guidelines and ensure proper underlayment, ventilation, and insulation for optimal performance and longevity. Consider consulting a professional roofer for the best advice on material selection and installation methods.