The content of the article
- What is a halogen lamp?
- Device
- Principle of operation
- Life time
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Types of Halogen Home Lamps
- Linear
- With outer box
- Capsule
- With reflector
- Low voltage
- How to choose a halogen lamp
- For the chandelier
- For spotlights
In order to replace conventional bulbs, they created an analog with high brightness, requiring a lower voltage in the network, suitable for standard socles. Halogen lamps differ from standard industrial fixtures, home chandeliers in terms of luminous flux and durability. They have found application in the manufacture of automotive headlights with high brightness, lighting devices operating from low voltage and having compact dimensions. You can order by mail or buy halogen lamps in any store – the goods are in demand.
What is a halogen lamp?
This is a special device for lighting rooms, working on the same principle as standard power fixtures. Halogen bulbs consist of a cap, an incandescent filament, a sealed bulb filled with gas. Atoms of a gaseous active substance react with an evaporating tungsten wire and immediately decompose under the influence of high temperature. This prevents the vaporized metal from settling on the walls of the flask. The advantage of such lamps is an extended service life..
Device
There are several types of capsule halogen bulbs that differ in bulb size, shape, and the presence of special reflectors. They are united by the typical structure of the cap, the chemical composition of the gas mixture, the presence of a tungsten wire, which provides a glow. Halogen lamps for spotlights and industrial lights can differ in voltage: they work equally efficiently from 220, 380 V and miniature electricity sources 6-100 V. The brightness of the light is easily regulated by a switch with a rheostat.
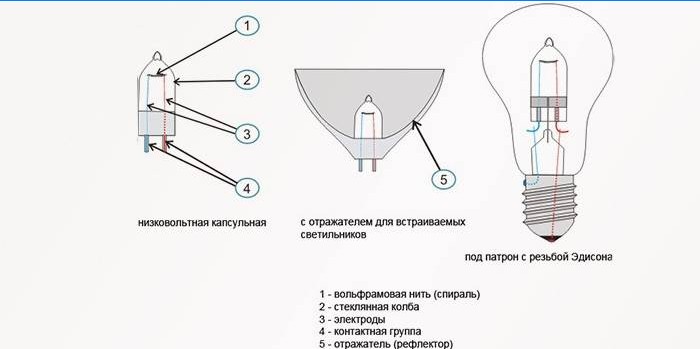
Principle of operation
The main difference from traditional lamps is the constant halogen-tungsten thread self-healing process. When heated, the wire slowly evaporates, as in an incandescent bulb. The gas inside the flask reacts with metal atoms, capturing them and not allowing them to settle on the walls. The peculiarity of the obtained compounds is the impossibility of their existence at high temperatures, therefore, a decomposition reaction occurs, followed by the deposition of tungsten atoms back onto the thread. With a decrease in power by a rheostat, the temperature drops, and self-healing stops.
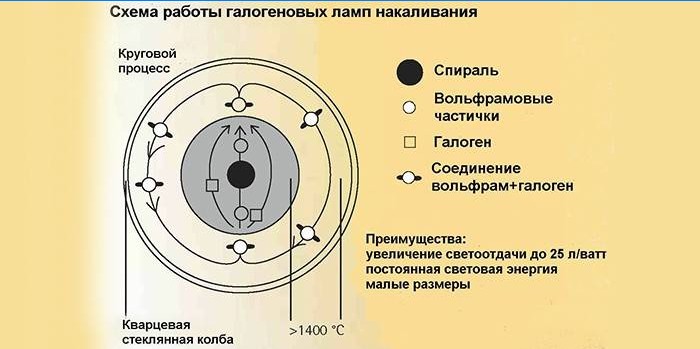
Life time
The glow temperature constantly maintains the incandescent filament due to the self-healing of tungsten by halogens in relative integrity. This increases the service life. The process is not ideal: the metal settles unevenly on the surface of the wire, thin sections gradually form. The average life of the device is 6000-7000 hours of continuous operation. Smooth inclusion through a rheostat increases it to 8000-12000 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages
Halogen lighting devices have a number of advantages and disadvantages arising from the features of the internal device, the principle of operation, and the possibility of operation. The pros include:
- Long service life.
- Stable operation, continuous light output.
- Increased efficiency compared to standard incandescent bulbs.
- Strength, resistance to mechanical damage.
- Small size.
- Reduced UV.
The disadvantages of this variety of lighting include:
- Fire hazard due to heating of the flask to high temperatures. Before checking the halogen lamp with a tester, let it cool.
- The gas mixture used in lamps is toxic to humans..
- Unusual white color lighting.
Types of Halogen Home Lamps
The range of halogen lamps is very wide: from low-voltage lamps to large spotlights that can illuminate the stadium. Home light bulbs are available in three varieties:
- With an external flask. Standard halogen lamps for a chandelier. External protection prevents fragmentation and gas spread after breaking.
- With reflector. Designed to create a directional light source. Used in car headlights, flashlights.
- Capsule. Miniature bulbs used in unprotected glass fixtures.

Linear
The device provides bright illumination of a large area without leaving dark corners, and additional protection from ultraviolet radiation makes the bulb safe. It is recommended to put on extensive storage facilities:
- model name: J 500W Camelion 2937;
- price: 64 r;
- characteristics: linear capsule, power 500 W, voltage 220 V, cap type R7s, luminous flux 9000 Lm;
- pluses: bright pure white light, a quartz flask reduces the amount of ultraviolet radiation;
- cons: a rare kind of cap.

An excellent example of an uninterrupted source of external lighting for streets, building facades, roads, sections of private sectors. Remember that models of this power are fire hazard if installed incorrectly:
- model name: HALOLINE 64740 1000W J189 Osram;
- price: 540 r;
- characteristics: tubular linear capsule, power 1000 W, voltage 220 V, cap R7s, luminous flux 22000 Lm;
- pluses: a large range of propagation of radiation;
- Cons: high color temperature 3000 K.

With outer box
The second capsule, installed in front of the main one, guarantees safety when the bulb burns out. The protective flask will not allow the gas to spread, and the debris will fly around the room:
- model name: Uniel E27 42 W;
- price: 70 r;
- characteristics: spherical protective capsule, power 42 W, voltage 220 V, luminous flux 670 Lm, cap E27;
- pluses: matte capsule;
- cons: it gets very hot outside.

The model exceeds standard incandescent lamps in efficiency by 30-40% with a total increase in radiation level. Save on energy by using halogen from electrostand:
- model name: Electrostand E14 42W;
- price: 35 r;
- characteristics: pear-shaped capsule, 42 W, 220 V, luminous flux 630 Lm, E14 base;
- pluses: low temperature;
- cons: not found.

Capsule
Small dimensions combined with a high level of light radiation make the model an ideal choice for lighting fixtures on jewelry stands. Install several of these nearby – and on the product you can see the smallest flaws:
- model name: JC 20W Camelion g4 12V 1955;
- price: 35 r;
- characteristics: low-voltage capsule, 12 V, 20 W, light output 320 Lm, diode base G4;
- pluses: powerful lighting;
- cons: not found.

The device is manufactured as a point source of light for suspended ceilings. Install small built-in shades at a distance of 80-100 cm – and the room will always be well lit:
- model name: SVETOZAR SV-44762-M;
- price: 30 r;
- characteristics: power 20 W, voltage 12 V, luminous flux 266 Lm, warm white, yellow;
- pluses: small sizes;
- cons: life time 2000 hours.

With reflector
A light bulb emitting a narrow beam of light of high brightness is ideal for the role of a lighting element of a headlamp or a flashlight. Low power consumption will not let you go without light at the wrong time:
- model name: COSMOS MR16 35W GU5.3 12V FMWc LKsmMR1612V35W;
- price: 50 r;
- characteristics: power 35 W, voltage 12 V, bulb MR16, service life 2000 hours;
- pluses: excellent lighting power 525 Lm;
- cons: not found.

Blocks of such illuminators are installed in the spotlights. It is also a good idea to mount these lamps in the ceiling to create a network of powerful spotlights:
- model name: SVETOZAR SV-44733;
- price: 60 r;
- characteristics: 35 W, 12 V, light power 652 Lm, spotlight capsule, GU5.3 base;
- pluses: good focusing of a light beam;
- cons: overheating.

Low voltage
The powerful stream of light that such a small device generates puts the model in a leading position on the list of the best lighting elements for flashlights. Install one such – and no darkness is terrible:
- model name: Navigator 94 204 MR16 50W 12V 2000h;
- price: 70 r;
- characteristics: 50 W, 12 V, warm white light (3300 K), GU5.3 base;
- pluses: high brightness;
- cons: power consumption, wear resistance of the thread.

COSMOS lamps with increased brightness are often installed on the external signs of stores, under glass display cases of stands. A 750 lux light source is guaranteed to attract attention:
- model name: COSMOS JC 50W G6.35 12V LKsmJC12V50W;
- price: 35 r;
- Features: 50 W, 12 V, JC bulb, G6.35 cap;
- pluses: light power 750 Lm;
- Cons: weak contacts.

How to choose a halogen lamp
To buy halogen lamps for the home, decide what requirements they must meet. There are a number of criteria by which you can determine which model of a lighting fixture you need:
- A kind of light bulb. Remember that linear halogen lighting fixtures are not suitable for the home. Other designs will be a good choice..
- Voltage. Unlike traditional incandescent lamps, the models in question have a wider range of capacities. Determine what voltage will be in the network that supplies the lamp.
- Flask material. Available are standard quartz models and made of tempered glass. The latter are better suited for living room lighting..
For the chandelier
Often you can find ceiling or wall lights, floor lamps, chandeliers equipped with halogen bulbs. The choice is justified: energy consumption is reduced, the level of illumination in the room increases. Learn how to buy a good lighting element for installation in a chandelier:
- The size of the flask. Make sure that the bulb does not get stuck in the lampshade – they differ in size from standard.
- Type of device. Choose varieties with an external bulb – they are ideal for household lighting.

For spotlights
The purpose of such special fixtures is to create a bright spot in a specific place. They are installed in several pieces at a short distance. Choose low-voltage halogen bulbs with reflectors: this variety forms a narrow beam of bright light. Choose the voltage and power, taking into account the number of installed devices.


I would like to understand the principle of operation and different types of halogen lamps suitable for residential use. Additionally, how can I determine the appropriate power and price range when selecting one? Thank you in advance for your help!
Halogen lamps operate by passing an electric current through a tungsten filament enclosed in a halogen gas-filled quartz bulb. The halogen gas helps to redeposit evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, increasing the lamp’s lifespan. There are various types of halogen lamps for residential use, such as PAR (parabolic aluminized reflector) lamps, MR (multifaceted reflector) lamps, and linear halogen lamps.
To determine the appropriate power, consider factors like room size and desired brightness level. 50-75 watts can be suitable for accent lighting, while 100-150 watts are common for general lighting. Prices vary based on the lamp type, wattage, and brand. Factors like energy efficiency, lifespan, and light output should also be considered when selecting a halogen lamp for residential use. Reading product specifications and comparisons can help you understand the power and price range that best fits your needs.
Can anyone explain how halogen lamps work and what are the different types suitable for household use? Also, what factors should one consider when choosing the power and price of a halogen lamp?
Halogen lamps contain a tungsten filament surrounded by a small amount of halogen gas. When the lamp is turned on, the filament heats up and emits light. The halogen gas helps redeposit evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, extending the lamp’s lifespan.
There are different types of halogen lamps suitable for household use, including PAR (parabolic aluminized reflector) lamps, MR (multifaceted reflector) lamps, and linear halogen tubes. When choosing a halogen lamp, one should consider the power rating (wattage) based on the desired brightness and the size of the space it will be used in. Additionally, consider the price, as higher wattage and more specialized types of halogen lamps may be more expensive. It is important to balance the desired brightness and energy efficiency with the cost when selecting a halogen lamp for household use.
Can you please provide more details on the principle of operation and different types of halogen lamps for household use? Additionally, I’m keen to know how to choose the appropriate power and price range while purchasing a halogen lamp.
Halogen lamps for household use operate on the principle of a tungsten filament enclosed in a quartz or high-temperature glass envelope containing halogen gases. When electricity passes through the filament, it heats up and emits light. The halogen gas helps to regenerate the tungsten, extending the lamp’s lifespan.
There are various types of halogen lamps including halogen incandescent lamps, halogen floodlights, and halogen reflector lamps. Halogen incandescent lamps are similar to traditional incandescent bulbs, while floodlights offer a wider beam for illumination of larger areas. Reflector lamps are designed to direct light in a specific direction, making them suitable for accent lighting or spotlighting.
When choosing the power of a halogen lamp, consider the desired brightness and the room or area size where it will be used. Higher wattage bulbs produce more light but consume more energy. It’s essential to balance your lighting needs with energy efficiency.
Price range varies depending on factors such as the brand, wattage, and additional features such as dimmability. While cheaper lamps may be attractive due to their low price, it is essential to balance cost with quality and longevity. Higher-quality lamps tend to be more durable and have a longer lifespan, making them cost-effective in the long run.
To choose an appropriate halogen lamp, consider the brightness requirements, room size, energy efficiency, desired features, and budget. Researching consumer reviews and comparing different brands and models can help you make an informed decision.
Can you please provide a detailed explanation of how halogen lamps work, including the principle of their operation? Additionally, I’d like to know what types of halogen lamps are suitable for home use. How can I determine the appropriate power and price when selecting a halogen lamp for my house? Thank you in advance for your assistance!
Halogen lamps work by using a tungsten filament enclosed in a quartz envelope filled with a small amount of a halogen gas, usually iodine or bromine. When the lamp is turned on, an electric current passes through the filament, heating it up. As the filament reaches a high temperature, it emits visible light.
The principle of a halogen lamp’s operation involves a process called the halogen cycle. As the filament heats up, tungsten particles evaporate and mix with the halogen gas, forming a halide vapor. This vaporizes the tungsten and prevents it from depositing on the inside of the bulb, which would cause the lamp to degrade quickly. Instead, the halide vapor migrates to cooler areas of the bulb, where it recombines with the tungsten, allowing the tungsten to be redeposited on the filament, thus extending the lamp’s lifespan.
For home use, there are various types of halogen lamps available. The most common ones are the PAR (Parabolic Aluminized Reflector) lamps, which provide bright and focused light. They are suitable for track lighting, recessed downlights, and outdoor floodlights. Another option is the MR (Multifaceted Reflector) lamps, which are commonly used in spotlights and accent lighting.
When selecting a halogen lamp for your house, consider the power and price appropriate for your needs. The power of the lamp is usually indicated in watts or lumens, and it determines the brightness of the light it emits. Assess the size of the room and the desired lighting level to determine the appropriate power. The price of the lamp depends on factors like brand, lifespan, and energy efficiency. Compare different options to find the best balance between quality and affordability.
In conclusion, halogen lamps work by heating a tungsten filament inside a quartz envelope using a halogen gas, with the halogen cycle ensuring the filament’s redeposition. PAR and MR lamps are suitable for home use, and determining the power and price involves considering the desired brightness, room size, and comparing different options.