Recommendation points
- What is the difference between a condensing boiler
- Design features and operating principle
- Application area
- Main manufacturers
- Installation of the condensing boiler
The heating equipment industry continues to delight with new, more advanced technical solutions. More and more gas boilers are entering the market, the declared performance of which is higher than that of standard units. Today we will deal with the reliability of such statements..
What is the difference between a condensing boiler
Condensing boilers are among those few representatives of power plants whose high efficiency indicators are not groundless. Unlike electrode boilers, cavitation heat generators and Meyer’s cells, a condensing boiler really has a conditional efficiency above unity. To understand the reasons for this, you should make a small excursion into thermal physics and take a closer look at the combustion of hydrocarbons.
Each type of fossil fuel has a specific calorific value, reflecting the amount of heat that is generated when one kilogram of a substance is burned. The data indicated in the calorific value tables were obtained under ideal bench conditions and in practice may differ, but the bottom line is that there is a limited amount of heat released during the oxidation reaction. At the same time, there are two types of combustion heat: higher and lower.
The products formed during the combustion of gas initially contain more energy than the boiler heat exchanger can absorb. Largely due to the decrease in the intensity of the heat flow with a decrease in the temperature difference, in part due to the rather short contact time of hot gases with the heat exchanger. These problems can be solved relatively easily by increasing the contact area of the heat exchanger, but there is also a third component – the energy stored by the water vapor generated during combustion. The energy that can be collected simply by cooling the combustion products is called the lowest, but if the energy is taken from the condensation of water vapor, the concept of the highest heat of combustion is applicable. The difference between these values is the basis for the over-unity of efficiency: as a result, the boiler absorbs not only the entire calculated heat of combustion, but also a part of the energy that was absorbed during the evaporation of water during combustion.
Design features and operating principle
In fact, there is nothing innovative in the design of individual units of the condensing boiler. If you look closely, many hot water and steam-water boilers installed in boiler houses of city heating systems can be called condensing boilers. They are united by the presence of an economizer – a coil with cold water through which combustion products are passed.
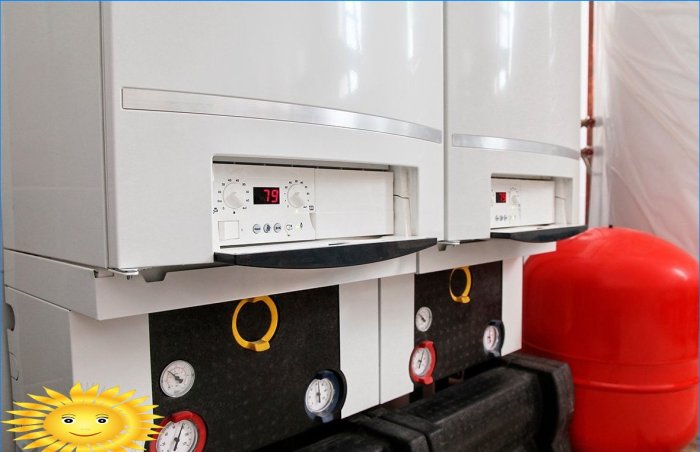
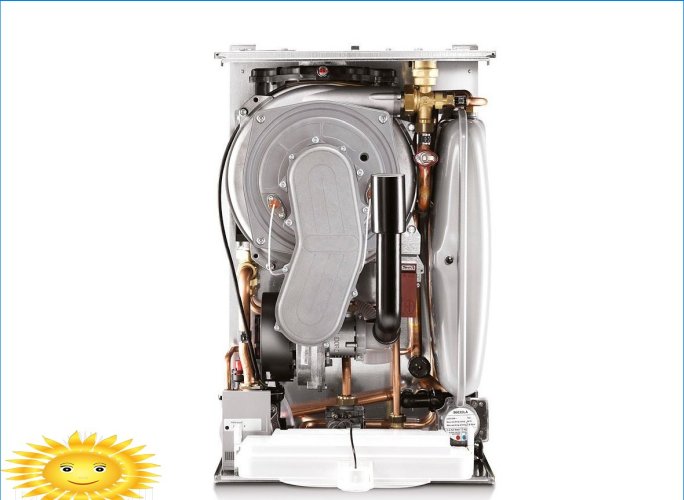
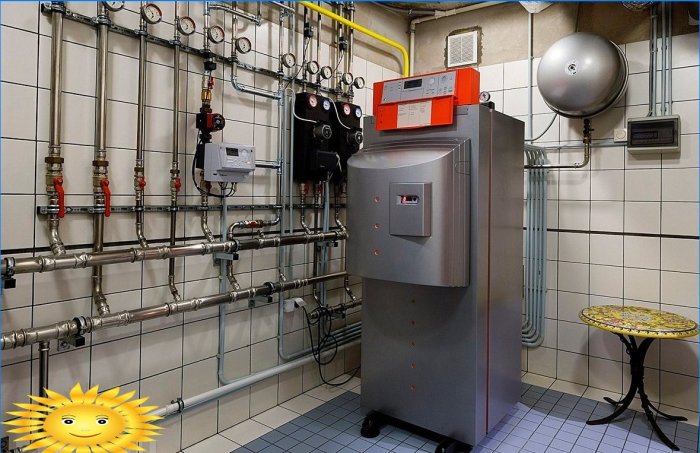
Modern condensing boilers are famous for the fact that the main heating and condensing units in them are placed inside a compact case, and the process of fuel combustion at all stages is controlled by smart electronics. There are both wall-mounted versions up to 100 kW and floor-standing boilers, the power of which is practically unlimited. The presence of several heat exchangers of complex shape creates an increased aerodynamic resistance, due to which most condensing boilers are also equipped with blowing fans and a number of additional technical devices.
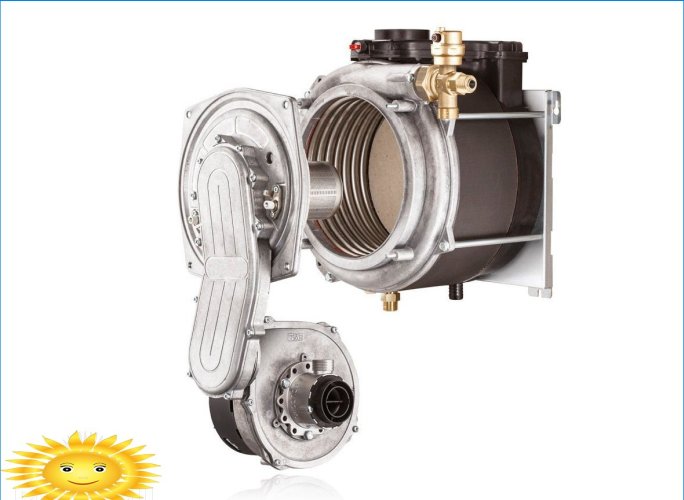
The boiler heat exchanger has several parallel circuits, for example, in Vaillant and Buderus, a radial coil is used, which resembles Buleryan’s convection pipes. The channels are arranged in three rows, the inner and middle ones absorb heat from a low-flame burner installed in the center of the heat exchanger. The external circuit is designed for condensation of water vapor.
In order to rationalize fuel consumption, the boiler electronics prepares a gas-air mixture with an average ratio of 1:13, regulating the gas supply and the blower fan speed. At the same time, air is passed through channels located close to the shell of the heating block and the smoke path, due to which the combustion products are cooled even more..
The electronics also registers the pressure drop in the second circuit and switches the three-way valve, directing the heating medium to the secondary DHW heat exchanger. Thus, the condensing boiler can only operate in one of the modes, and when the second circuit is heated, the condensation effect is practically not pronounced.
Application area
Condensing boilers are designed to operate at a fairly low coolant temperature. As a rule, this is no more than 40 ° C in the return line to 60 ° C in the supply. The ideal ratio is considered to be 30/50 ° C, but for stable operation in such modes, it is required that the heating system is initially designed with the expectation that the heat generator will be represented by a specific type of boiler.
At a minimum, a more developed network of radiators is required, the heat transfer of which directly depends on the temperature of the coolant. Practice shows that in order to achieve the same values of heat dissipated on radiators, the total number of their sections must be increased by at least 25%. But at the same time, the inertia of the system is much less critical: the condensing boiler works almost without interruption, therefore, there are no temperature drops in the heated rooms. Because of this, this type of heating unit is recommended for use in frame houses with a low energy balance, but not because of the efficiency above unity, but because of the specific operating mode.
It is also obvious that, due to the low temperatures of the heating medium, condensing boilers are ideal for operation in liquid underfloor heating systems. In such cases, the use of such a heat source is more than justified: the organization of a thermostatic unit is not required, and the low temperature in the return line guarantees high performance of the condensing heat exchanger. At the same time, compliance with the basic requirements for the inertia of the system is guaranteed due to the presence of a sufficiently massive underfloor heating screed.
Main manufacturers
There is a lot of controversy about the advisability of purchasing a condensing boiler. On the one hand, on the face, although not significant, but still an increase in efficiency. On the other hand, due to more gentle temperature conditions, the service life of the heating unit increases. With the difference between conventional and condensing boilers of the same manufacturer in 20-30% and service life of about 20 years or more, this technique fully pays off in most cases.
In the upper price segment, condensing boilers are mainly represented by European manufacturers: Bosch, Buderus, Viessmann, Vaillant. There is little fundamental difference in reliability, efficiency and ease of use between them, so in the end the consumer starts from the price and availability, as well as from the current trade offers. At a cost of about 60-100 thousand rubles, the average power of premium condensing boilers is about 25 kW.
Cheaper options are supplied to the heating equipment market by BAXI, Ariston, Demrad and similar manufacturers. Boilers have a relatively shorter service life, mostly due to imperfect heat exchanger design and low quality steel. The most budgetary options are supplied by Protherm and Ferroli, equipment of this class is available at a price of about 35 thousand rubles with a power of about 20 kW. As a rule, cheap boilers do not have a secondary circuit and a galvanic coating of the heat exchanger, which is resistant to aggressive condensate. Cheap boilers are supplied with less advanced electronics and, in general, in terms of reliability are much inferior to the representatives of the middle price segment.
Installation of the condensing boiler
The rules for the installation, commissioning and maintenance of condensing boilers are based on the standards and principles that also apply to conventional gas appliances. The equipment is accompanied by a detailed installation and operation manual, we will only give you the key differences and nuances that require mandatory compliance.
The installation of the boiler can be wall-mounted and floor-standing, there is no fundamental difference in that, you just need to observe the minimum permissible indents from walls and other stationary objects for the possibility of equipment maintenance. Standard requirements for flammability of walls and bases also apply..
Condensing boilers have a closed combustion chamber isolated from the room environment. Air supply to the room is usually required for installations with a power of over 100 kW. The flue gas removal system is represented by a sealed coaxial flue according to DIN 18160, as a rule, standard size 70/100 is used. Chimneys from standard boilers are not suitable, only special systems must be used. Also, when determining the configuration of the exhaust duct, it is imperative to comply with the requirements for the design of chimneys set forth in the installation manual..
When operating a gas boiler with a capacity of 20-25 kW, about 30 liters of condensate are formed per day. The equipment has a drain pipe with a built-in siphon; a pipe with a certain minimum nominal bore must be laid from it to the nearest discharge point into the sewer. If liquid fuel is used or there is a recommendation from the gas supplier, the condensate should be drained through a neutralizer.
The boiler connection is standard: gas is supplied from a rigid stave through a bellows hose with the obligatory installation of a gas ball valve with a fire cutoff. Single-phase power supply, protective conductor connection required. High-quality boilers have built-in protection against overload and voltage surges; for cheaper equipment, stabilization may be required. You also need to pay attention that many boilers have additional terminals for connecting a DHW recirculation pump, temperature sensors, a gas valve and other auxiliary devices..
For the most part, condensing boilers include all attachments necessary for the stable operation of the general heating circuit, including a safety group, an expansion tank and a circulation pump. If the installation of such devices is not provided for by the instructions, they do not need to be mounted, otherwise the system operation modes may be violated. When designing heating, it is recommended to refer to the last pages of the manual, where the permissible boiler switching schemes in systems of different configurations are determined..










What are the main advantages of gas condensing boilers and how do they differ from traditional boilers in terms of efficiency and performance?
What are the different options available for gas condensing boilers and what are the advantages of choosing them over other types of boilers?